BACK
2023 / 12 / 25
Moth flies are insects from the Family Psychodidae, Order Diptera, which are the relatives of flies, mosquitoes, and fruit flies. They are also called “drain fly” because they usually appear around the sewer openings. They are often be seen in washrooms, they are also known as "washroom bugs" in Taiwan. There are more than 30 species of moth flies recorded in Taiwan, several of which are quite common nuisance pests that appear in or around various domestic or commercial buildings.
Adult moth flies may breed in large numbers indoors, and then gather around windows, lamps, showers, bathtubs, washbasins, and floor drain holes, making people feel uncomfortable. Most people don’t know where moth flies breed. The recurring appearance of moth flies is therefore disturbing to many people. Although moth flies do not transmit specific epidemics like Aedes mosquitoes, they are similar to flies and breed in unhygienic environments, so there is a risk of spreading pathogens and affecting human health.
Adult moth flies may breed in large numbers indoors, and then gather around windows, lamps, showers, bathtubs, washbasins, and floor drain holes, making people feel uncomfortable. Most people don’t know where moth flies breed. The recurring appearance of moth flies is therefore disturbing to many people. Although moth flies do not transmit specific epidemics like Aedes mosquitoes, they are similar to flies and breed in unhygienic environments, so there is a risk of spreading pathogens and affecting human health.
The common species, the Clogmia albipunctatus, has a body length of about 3 - 4 mm. The body surface is covered with very long hairs. The wings are very large compared to the body. When it rests on the solid surface, the wings are folded up like a moth. The flying ability of moth flies are very poor, they spend most of their time on the surface of objects and will land again after flying for more than 1 meter. The larvae are worm-like, without legs but with a breathing tube structure that allows them to hide in organic matter.
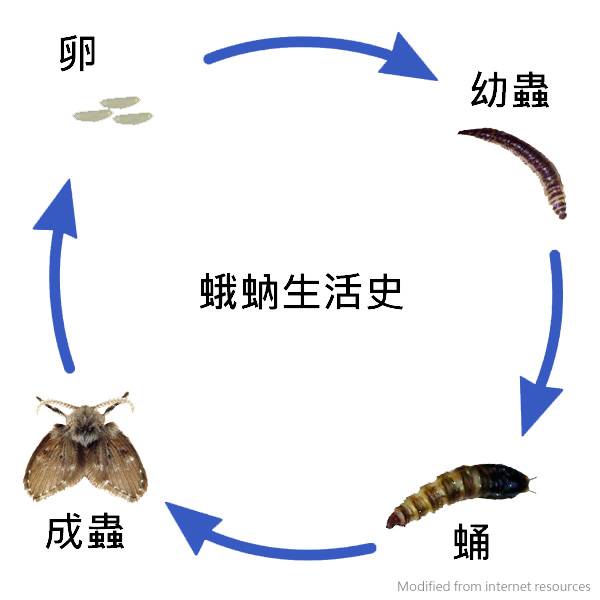
The life cycle of moth fly
Moth fly larvae grow in shallow sewage or highly moist organic matters. Sewage drain pipes, air conditioning condensate drain pipes, sewage filter tanks, septic tanks and moist compost often have condensation and gelatinous organic matter films deposited on the inside of the pipes, where eggs, larvae and pupae of moth flies may be deposited. Other breeding sources include dirty trash cans, tree holes, rainwater recycling systems, or low-lying locations around buildings, where stagnant water can easily lead to the growth of algae and mold. The female will lay about 10-200 eggs on these moist organic debris. The eggs will hatch in less than 2 days, and the larvae will feed on these organic materials and algae for 9-15 days, and then the larvae will pupate on the surface of the breeding source and emerge in about 2 days.
The life cycle of moth fly
Moth fly larvae grow in shallow sewage or highly moist organic matters. Sewage drain pipes, air conditioning condensate drain pipes, sewage filter tanks, septic tanks and moist compost often have condensation and gelatinous organic matter films deposited on the inside of the pipes, where eggs, larvae and pupae of moth flies may be deposited. Other breeding sources include dirty trash cans, tree holes, rainwater recycling systems, or low-lying locations around buildings, where stagnant water can easily lead to the growth of algae and mold. The female will lay about 10-200 eggs on these moist organic debris. The eggs will hatch in less than 2 days, and the larvae will feed on these organic materials and algae for 9-15 days, and then the larvae will pupate on the surface of the breeding source and emerge in about 2 days.
How to control moth flies
To control moth flies, it is not enough to simply kill the adults. It is necessary to find and eliminate the source of breeding, such as finding the above-mentioned moist and larval food sources to cure the root cause.
Outdoor breeding sources or infested areas include:
Damaged or faulty septic tank lines, rain or air conditioner condensation causing water accumulation. If it is a shaded place, the soil or foundation is prone to algae and mold growth; if no breeding source of moth flies can be found there, then moth flies may also have invaded along the airflow from a neighboring sewage system or a faulty septic line.
Indoor moth fly infestation areas include:
Toilets (around the toilet tank), sinks, bathtub and shower drains, floor drains, ice machine condensate discharge pipes, and loose floor tiles can easily harbor dirt.
If you want to confirm which drain hole the moth flies are flying out of at the location where the moth flies are infested, you can use a plastic container that can completely cover the drain hole, such as a disposable dish or pudding cup, and coat it with a thin layer of Vaseline. Come over and cover the drain outlet without leaving any gaps. After leaving it for a night or longer, check whether there are any moth flies trapped on the Vaseline, and you can roughly confirm the invasion point. If you are a professional pest control operator, a good detection tool is a light trap. Adult moth flies will be attracted and captured by the stick board or fan on the light trap. After inspection, more precise prevention and control can be carried out.
Professional pest control technicians could use foam formulations of pesticides. This is a method of adding foaming additives to water-based pesticides and then applying by special foam equipment. This allows the pesticides to stay at the application site for a period of time, including some hollow or vertical positions, such as back of the drainage hole or pipe wall, it can also reduce the waste of insecticides.
In addition, it is recommended that the larvae of moth flies can be controlled with Sumilarv® Insect Growth Regulator granules. Sumilarv® granules need to settle in the water body to slowly release the active ingredients attached to the pharmaceutical granules. We need to calculate the usage amount in advance and pour it into the toilet (not the water tank) and flush the granules into the septic tank, or pour the pellets directly into the drain line. The juvenile hormone concentration in moth fly larvae will be disturbed by Sumilarv®, causing them to fail to emerge normally. Larval control insecticides like Sumilarv® cannot control existing adult insects, but we can use general aerosol insecticides to spray directly on the adult insects, or spray them on the surface where they will rest.
In addition to applying pesticides, cleaning dirty pipes or surfaces that provide shelter and food for larvae can effectively control the population, and regular cleaning can prevent future recurrences. For toilets and urinals, it is better to use enzyme or biodegradable cleaners, because highly corrosive acid-base cleaners may damage pipelines and septic tank functions.
To control moth flies, it is not enough to simply kill the adults. It is necessary to find and eliminate the source of breeding, such as finding the above-mentioned moist and larval food sources to cure the root cause.
Outdoor breeding sources or infested areas include:
Damaged or faulty septic tank lines, rain or air conditioner condensation causing water accumulation. If it is a shaded place, the soil or foundation is prone to algae and mold growth; if no breeding source of moth flies can be found there, then moth flies may also have invaded along the airflow from a neighboring sewage system or a faulty septic line.
Indoor moth fly infestation areas include:
Toilets (around the toilet tank), sinks, bathtub and shower drains, floor drains, ice machine condensate discharge pipes, and loose floor tiles can easily harbor dirt.
If you want to confirm which drain hole the moth flies are flying out of at the location where the moth flies are infested, you can use a plastic container that can completely cover the drain hole, such as a disposable dish or pudding cup, and coat it with a thin layer of Vaseline. Come over and cover the drain outlet without leaving any gaps. After leaving it for a night or longer, check whether there are any moth flies trapped on the Vaseline, and you can roughly confirm the invasion point. If you are a professional pest control operator, a good detection tool is a light trap. Adult moth flies will be attracted and captured by the stick board or fan on the light trap. After inspection, more precise prevention and control can be carried out.
Professional pest control technicians could use foam formulations of pesticides. This is a method of adding foaming additives to water-based pesticides and then applying by special foam equipment. This allows the pesticides to stay at the application site for a period of time, including some hollow or vertical positions, such as back of the drainage hole or pipe wall, it can also reduce the waste of insecticides.
In addition, it is recommended that the larvae of moth flies can be controlled with Sumilarv® Insect Growth Regulator granules. Sumilarv® granules need to settle in the water body to slowly release the active ingredients attached to the pharmaceutical granules. We need to calculate the usage amount in advance and pour it into the toilet (not the water tank) and flush the granules into the septic tank, or pour the pellets directly into the drain line. The juvenile hormone concentration in moth fly larvae will be disturbed by Sumilarv®, causing them to fail to emerge normally. Larval control insecticides like Sumilarv® cannot control existing adult insects, but we can use general aerosol insecticides to spray directly on the adult insects, or spray them on the surface where they will rest.
In addition to applying pesticides, cleaning dirty pipes or surfaces that provide shelter and food for larvae can effectively control the population, and regular cleaning can prevent future recurrences. For toilets and urinals, it is better to use enzyme or biodegradable cleaners, because highly corrosive acid-base cleaners may damage pipelines and septic tank functions.

