BACK
2023 / 12 / 25
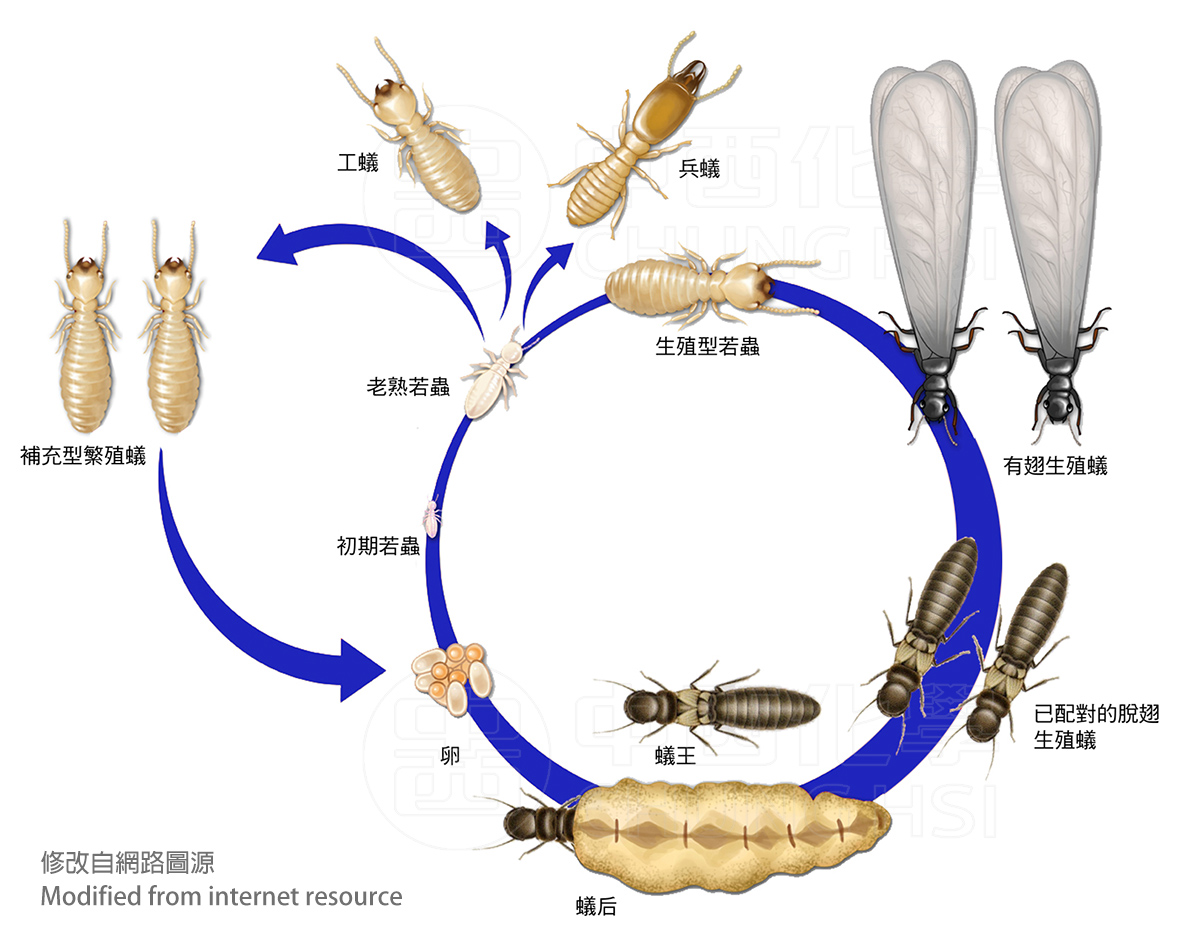
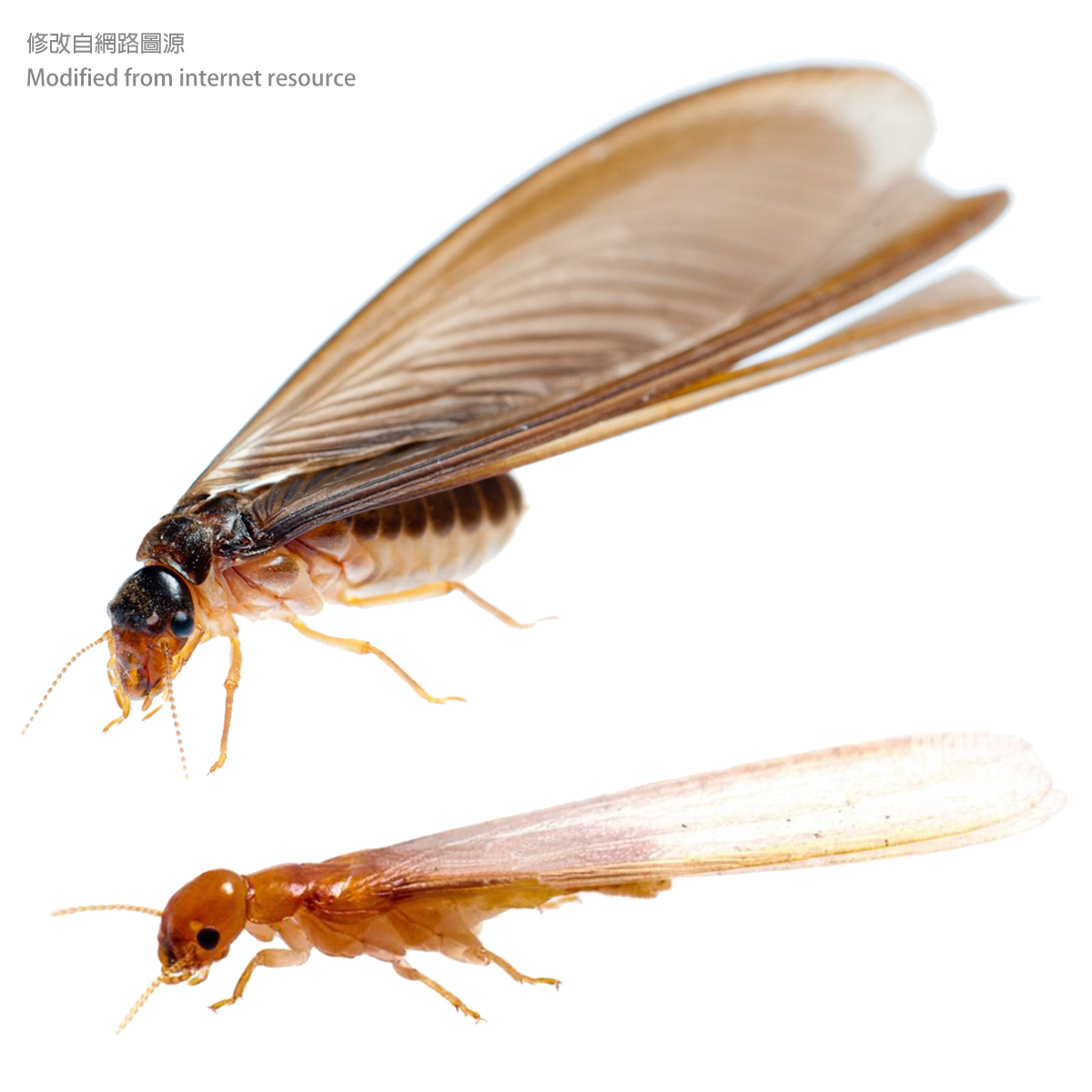
Many people have seen the seasonal sight of "big water ants" (in Taiwanese), lots of flying insects that swarm around lights. But in fact, these "big water ants" are the future kings and queens of termites waiting to mate (the winged individuals of ants are more easily seen in suburbs). It is difficult to associate these flying insects with the termites that eat wood and destroy decorations and furniture in the house.
Termites were once classified in the order Isoptera, meaning that the shape and form of the two pairs of wings of winged individuals are very similar. However, in recent years, termites have been generally recognized as "social cockroaches" and have been classified under the class Insecta, order Blattaria, family Termitoidae, while the order Isoptera no longer exists.
Both termites and ants have the word "ant" in their names in different cultures and languages, such as Chinese and Japanese, if you directly translate the name to English, both will be the "white ant". But termites and ants are actually very different. Ants are insects of the order Hymenoptera, and they undergo complete metamorphosis (egg → larva → pupa → adult), and are more closely related to wasps; termites undergo incomplete metamorphosis (progressively), and their social lifestyle and class division of labor are similar to those of ants, but quite different.
Termites were once classified in the order Isoptera, meaning that the shape and form of the two pairs of wings of winged individuals are very similar. However, in recent years, termites have been generally recognized as "social cockroaches" and have been classified under the class Insecta, order Blattaria, family Termitoidae, while the order Isoptera no longer exists.
Both termites and ants have the word "ant" in their names in different cultures and languages, such as Chinese and Japanese, if you directly translate the name to English, both will be the "white ant". But termites and ants are actually very different. Ants are insects of the order Hymenoptera, and they undergo complete metamorphosis (egg → larva → pupa → adult), and are more closely related to wasps; termites undergo incomplete metamorphosis (progressively), and their social lifestyle and class division of labor are similar to those of ants, but quite different.

The social structure of termites can be divided into reproductive classes: king, queen, and supplementary reproductives (secondary reproductive individuals), and non-reproductive classes: workers and soldiers. The status and division of labor of male termites in the colony are relatively equal to those of female termites, and there are both male and female workers and soldiers. The termite king can survive for a long time and provide sperm to the queen. The termite queen is a long-lived egg-laying machine. She drags her swollen abdomen and can't go anywhere. She lays eggs continuously in a small chamber in the nest throughout her life.
Termites can be divided into three categories based on their ecological habits: subterranean termites, drywood termites and dampwood termites. Among them, subterranean termites are the most common pests, with a large population and the speed at which damage is manifested is also fast, such as the Formosan termite (Coptotermes formosanus) and Asian subterranean termite (C. gestroi). Drywood termites are less serious pests that often eat into wooden structures and furniture, leaving behind gritty droppings. According to statistics in 2003, the economic losses caused by subterranean termites and drywood termites worldwide are approximately US$2 billion, and in Southeast Asia alone, the losses caused by termites each year (including control costs) are approximately US$400 million. This should also include secondary costs caused by improper handling. Dampwood termites have almost nothing to do with human economic activities. On the contrary, they are beneficial to the ecology and are indispensable organisms because they accelerate the decomposition of rotten wood and fallen leaves in the wild and are also food source for many animals.
Termites can be divided into three categories based on their ecological habits: subterranean termites, drywood termites and dampwood termites. Among them, subterranean termites are the most common pests, with a large population and the speed at which damage is manifested is also fast, such as the Formosan termite (Coptotermes formosanus) and Asian subterranean termite (C. gestroi). Drywood termites are less serious pests that often eat into wooden structures and furniture, leaving behind gritty droppings. According to statistics in 2003, the economic losses caused by subterranean termites and drywood termites worldwide are approximately US$2 billion, and in Southeast Asia alone, the losses caused by termites each year (including control costs) are approximately US$400 million. This should also include secondary costs caused by improper handling. Dampwood termites have almost nothing to do with human economic activities. On the contrary, they are beneficial to the ecology and are indispensable organisms because they accelerate the decomposition of rotten wood and fallen leaves in the wild and are also food source for many animals.
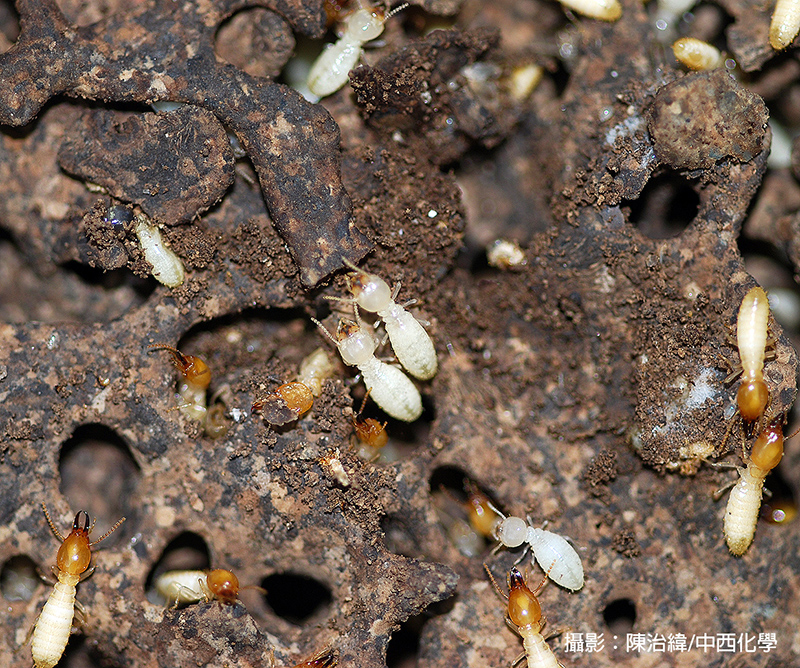

Why it is difficult to control termites?
Common household pests such as cockroaches, mosquitoes, and flies may exist in high density, but they are usually just independent individuals that happen to appear in the same place at the same time. Once attacked, they can only flee in panic without taking care of their own lives, so they are not too difficult to prevent and control. Social insects live in groups and cooperate with each other, and a colony is filled with closely related family members. If they cannot mount an effective resistance, they will conduct an organized retreat to avoid the extermination of the colony.
Both subterranean termites and drywood termites are very secretive insects. When they are discovered, they have already caused some damage. If the characteristics of social insects are ignored when taking preventive measures at this time, and if the wrong strategy is adopted, the control progress will often turn into a long-term battle.
Common household pests such as cockroaches, mosquitoes, and flies may exist in high density, but they are usually just independent individuals that happen to appear in the same place at the same time. Once attacked, they can only flee in panic without taking care of their own lives, so they are not too difficult to prevent and control. Social insects live in groups and cooperate with each other, and a colony is filled with closely related family members. If they cannot mount an effective resistance, they will conduct an organized retreat to avoid the extermination of the colony.
Both subterranean termites and drywood termites are very secretive insects. When they are discovered, they have already caused some damage. If the characteristics of social insects are ignored when taking preventive measures at this time, and if the wrong strategy is adopted, the control progress will often turn into a long-term battle.
Termites have the biological characteristic of avoiding the corpses of their companions. If a large number of working class die quickly in the mud tunnels built outside the termite nest, other termites will quickly close the paths that have been sprayed with pesticides and have many corpses, and respond according to the degree of harassment. People often spray insecticides to termites and think they have eliminated the termites after seeing many of them die. However, they do not realize that this only kills the visible individuals on the periphery. The termites and their queens cannot be eradicated unless eradicating them deep inside the colony. People usually do not have such knowledge, tools, experience and skills of termite control. This is why termite elimination still requires technicians from professional pest control companies to handle it.
What you need to know about termites once you want to control them
. Termites are difficult to eradicate not because they develop resistance to insecticides, but because the controls are inaccurate or the methods are wrong.
. Termites are photophobic, expand gradually, are sensitive to vibrations, and prefer warm, unventilated and humid environments.
. If your environmental conditions happen to be those preferred by termites, the chances of being invaded multiple times by termites will greatly increase.
. The covering tunnels that termites build with mud are to maintain humidity and block light, so termites will not appear in front of people.
. Termites usually spread outward from deep within the colony, and the termites that can be seen directly are only a small part of the entire colony.
. By the time termites are seen, the damage is usually already there and may be worse than expected.
. The termite queen does not commands. She just hides in the deepest part of the nest and is responsible for laying eggs. Even if the old queen dies, there will be backup reproductive individuals to inherit her egg-laying job.
. Spraying, fumigating, or injecting termites with household insecticides can indeed kill or drive away some termites, but if you don't kill the reproductive individuals deep in the nest, termites will be difficult to eradicate. Otherwise, if you kill one hundred termites, there will be thousands and millions of termites ready to take its place.
. Termites are difficult to eradicate not because they develop resistance to insecticides, but because the controls are inaccurate or the methods are wrong.
. Termites are photophobic, expand gradually, are sensitive to vibrations, and prefer warm, unventilated and humid environments.
. If your environmental conditions happen to be those preferred by termites, the chances of being invaded multiple times by termites will greatly increase.
. The covering tunnels that termites build with mud are to maintain humidity and block light, so termites will not appear in front of people.
. Termites usually spread outward from deep within the colony, and the termites that can be seen directly are only a small part of the entire colony.
. By the time termites are seen, the damage is usually already there and may be worse than expected.
. The termite queen does not commands. She just hides in the deepest part of the nest and is responsible for laying eggs. Even if the old queen dies, there will be backup reproductive individuals to inherit her egg-laying job.
. Spraying, fumigating, or injecting termites with household insecticides can indeed kill or drive away some termites, but if you don't kill the reproductive individuals deep in the nest, termites will be difficult to eradicate. Otherwise, if you kill one hundred termites, there will be thousands and millions of termites ready to take its place.

